InForSec定于2021年8月27日(周五)下午在线直播“网络空间安全国际学术成果分享(中)”活动。本次学术活动将邀请在网络空间安全顶级会议上发表论文的研究者分享他们的最新研究成果,并就研究过程中的灵感、经验和体会进行深入交流。此次邀请的议题覆盖网安研究领域的诸多前沿问题,包括“信息物理系统安全(Cyber Physical System Security)”以及“软件安全(Software Security)”。
主题:网络空间安全国际学术成果分享(中)
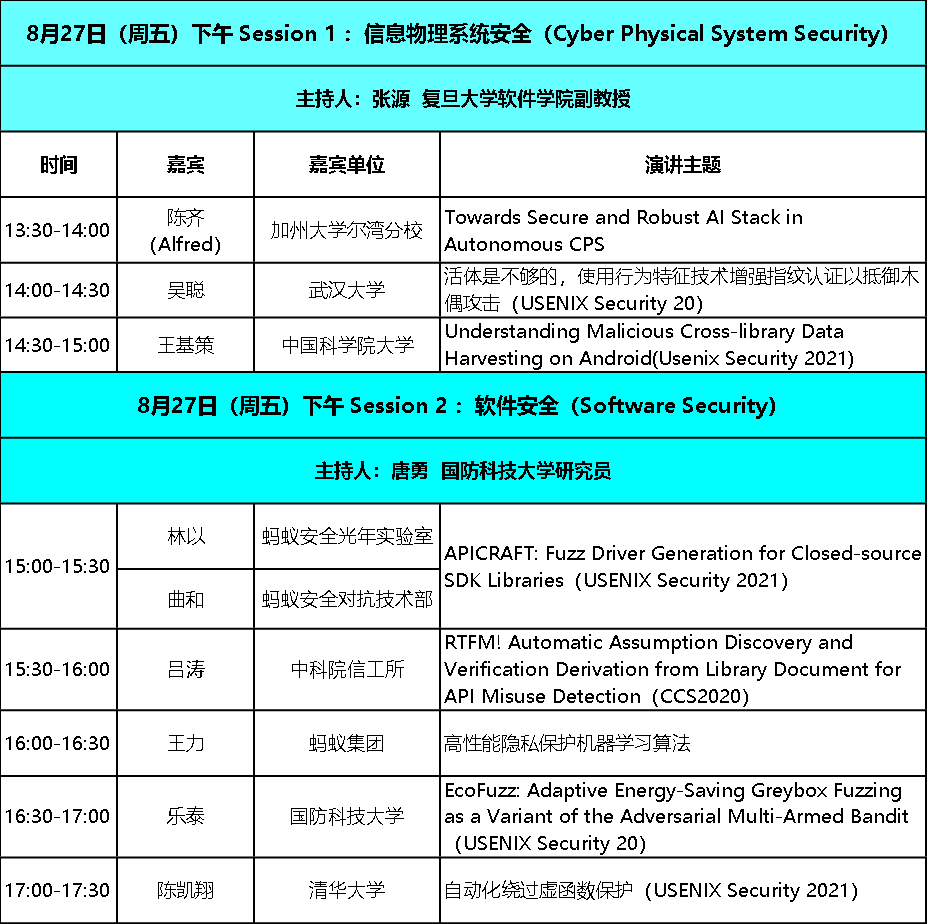
时间:2021年8月27日 13:30-18:00
主办:
网络安全研究国际学术论坛(InForSec)
承办:
清华大学网络科学与网络空间研究院
复旦大学系统软件与安全实验室
协办:
北京信息科学与技术国家研究中心
中国科学院大学国家计算机网络入侵防范中心
中国科学院计算技术研究所计算机体系结构国家重点实验室
百度安全
奇安信集团
蚂蚁集团
直播地址:
BCS2021大会在线直播二维码

会议日程
嘉宾介绍
陈齐 加州大学尔湾分校助理教授

演讲主题:Towards Secure and Robust AI Stack in Autonomous CPS
内容摘要:
Autonomous CPS (Cyber-Physical System) systems consist of both cyber and physical components working jointly to achieve highly automated operations in the physical world. Notable examples of such systems include Autonomous Driving (AD) vehicles and delivery drones/robots, which are increasingly deployed and commercialized in the real world. Specifically, AD technology has always been an international pursuit due to its significant benefit in driving safety, efficiency, and mobility. Over 15 years after the first DARPA Grand Challenge, its development and deployment are becoming increasingly mature and practical, with some AD vehicles already providing services on public roads (e.g., Google Waymo in Phoenix and Baidu Apollo in China). In AD technology, the AI stack, or the AD software, is highly security critical: it is in charge of safety-critical driving decisions such as collision avoidance and lane keeping, and thus any security problems in it can directly impact road safety. In this talk, I will describe my recent research that initiates the first systematic effort towards understanding and addressing the security problems in industry-grade AD software. I will be focusing on two critical modules: perception and localization, and talk about how we are able to discover novel and practical sensor/physical-world attacks that can cause end-to-end safety impacts such as crashing into obstacles or driving off road. I will also briefly talk about my recent research on AI stack security in smart transportation in general, especially those enabled by Connected Vehicle (CV) technology. I will conclude with a discussion on defense and future research directions.
嘉宾简介:
Qi Alfred Chen is an Assistant Professor in the Department of Computer Science at the University of California, Irvine. His research interest spans software security, systems security, and network security. Currently, his research focuses on security problems in autonomous CPS and IoT systems (e.g., autonomous driving and intelligent transportation). His works have high impacts in both academic and industry with over 30 research papers in top-tier venues in security, mobile systems, transportation, software engineering, and machine learning; a nationwide USDHS US-CERT alert, and multiple CVEs; over 50 news articles by major news media such as Forbes, Fortune, and BBC News; and vulnerability report acknowledgments from USDOT, Apple, Microsoft, Comcast, Daimler, etc. Recently, his research triggered over 25 autonomous driving companies to start security vulnerability investigations; some confirmed to work on fixes. He serves as reviewers for various top-tier venues such as Usenix Security, ACM CCS, NDSS, TIFS, TDSC, T-ITS, etc., and co-found the AutoSec workshop (co-located with NDSS’21). He received various awards such as NSF CRII Award, NDSS’19 and NDSS’20 best poster awards, UCI Chancellor’s Award for mentoring, and UM Distinguished Dissertation Award. His group won the 1st place in the first AutoDriving Security CTF (part of BCTF) in 2020. Chen received his Ph.D. from the University of Michigan in 2018.
吴聪 武汉大学国家网络安全学院博士生

演讲主题:Liveness is Not Enough: Enhancing Fingerprint Authentication with Behavioral Biometrics to Defeat Puppet Attacks
活体是不够的,使用行为特征技术增强指纹认证以抵御木偶攻击
内容摘要:
Fingerprint authentication has gained increasing popularity on mobile devices in recent years. However, it is vulnerable to presentation attacks, which include that an attacker spoofs with an artificial replica. Many liveness detection solutions have been proposed to defeat such presentation attacks; however, they all fail to defend against a particular type of presentation attack, namely puppet attack, in which an attacker places an unwilling victim’s finger on the fingerprint sensor. In this paper, we propose FINAUTH, an effective and efficient software-only solution, to complement fingerprint authentication by defeating both synthetic spoofs and puppet attacks using fingertip-touch characteristics. FINAUTH characterizes intrinsic fingertip-touch behaviors including the acceleration and the rotation angle of mobile devices when a legitimate user authenticates. FINAUTH only utilizes common sensors equipped on mobile devices and does not introduce extra usability burdens on users. To evaluate the effectiveness of FINAUTH, we carried out experiments on datasets collected from 90 subjects after the IRB approval. The results show that FINAUTH can achieve the average balanced accuracy of 96.04% with 5 training data points and 99.28% with 100 training data points. Security experiments also demonstrate that FINAUTH is resilient against possible attacks. In addition, we report the usability analysis results of FINAUTH, including user authentication delay and overhead.
近年来,指纹认证在移动设备越来越受欢迎,被称为最受用户青睐的身份认证方式。然而,在实际使用的环节中,它易受到展示攻击(Presentation attack)的威胁,例如攻击者利用人工复制品(硅胶脂等)欺骗指纹传感器以绕过指纹认证系统的检测。对此,众多研究学者提出了基于软件和硬件的方法以防御展示攻击,这些方法的关注更多的是指纹活体检测,即检测输入的指纹是否有生命特征。然而,现有的活体检测方法无法防御指纹认证中被忽视的木偶攻击:攻击者在用户无意识的情况(如熟睡或昏厥)下,将用户的真实指纹放在指纹传感器上以绕过指纹认证系统。针对该问题,我们设计了一种基于行为特征的指纹认证增强方案FINAUTH。当用户在执行指纹认证的时候,通过分析指尖触摸(fingertip-touch)的行为特征判断当前输入指纹的用户是否为合法用户。FINAUTH仅依赖于的移动设备上常见传感器,不会给用户带来额外的操作负担。实验表明,本方案能够以较高的准确度进行用户身份认证,同时在不破坏实用性的情况下,达到有效防御木偶攻击的目标。
嘉宾简介:
武汉大学国家网络安全学院2017级博士生,目前研究方向为移动终端身份认证、生物认证。
王基策 中国科学院大学计算机学院博士生

演讲主题:Understanding Malicious Cross-library Data Harvesting on Android
内容摘要:
Recent years have witnessed the rise of security risks of libraries integrated in mobile apps, which are reported to steal private user data from the host apps and the app backend servers. Their security implications, however, have never been fully understood. In our research, we brought to light a new attack vector long been ignored yet with serious privacy impacts – malicious libraries strategically target other vendors’ SDKs integrated in the same host app to harvest private user data (e.g., Facebook’s user profile). Using a methodology that incorporates semantic analysis on an SDK’s Terms of Services (ToS, which describes restricted data access and sharing policies) and code analysis on cross-library interactions, we were able to investigate 1.3 million Google Play apps and the ToSes from 40 highly-popular SDKs, leading to the discovery of 42 distinct libraries stealthily harvesting data from 16 popular SDKs, which affect more than 19K apps with a total of 9 billion downloads. Our study further sheds light on the underground ecosystem behind such library-based data harvesting (e.g., monetary incentives for SDK integration), their unique strategies (e.g., hiding data in crash reports and using C2 server to schedule data exfiltration) and significant impacts.
移动应用开发过程中嵌入了大量的第三方库,它们丰富了移动应用的功能,但是也引入了许多安全风险,例如从移动设备及应用后端服务器窃取用户隐私数据。然而,现有研究并不充分,我们的研究揭示了一个新的严重威胁用户隐私的攻击向量——恶意第三方库攻击集成于同一应用程序中的其他第三方库,以获取用户隐私数据(Malicious Cross-library Data Harvesting)。通过分析目标第三方库的服务条款(ToS, 描述了数据访问与共享政策)以及应用程序中的跨库交互行为,我们检测了Google Play市场上的130万个移动应用。结果发现,42个恶意库从16个流行的第三方库中窃取数据,影响了超过19K个应用,研究进一步揭示了这种数据收集行为背后的地下生态系统,它们独特的数据收集策略及其重要影响。
嘉宾简介:
中国科学院大学计算机学院博士生。主要研究方向为移动安全,漏洞挖掘等。
林以(@xwlin_roy) 蚂蚁安全光年实验室安全研究员

曲和 蚂蚁安全对抗技术部负责人

演讲主题:APICRAFT: Fuzz Driver Generation for Closed-source SDK Libraries
内容摘要:
针对应用库的 fuzzing 需要 fuzz driver 作为入口。fuzz driver 作为 fuzzing 的入口程序,调用需要被 fuzzing 的应用库的 API,来接收来自 fuzzer 的输入。实际上,fuzz driver 均是由安全专家所构建,其质量取决于作者的专业性以及对目标攻击面的熟悉度。业界当前已经提出了相关的技术来自动化生成 fuzz driver来减轻人工工作量并确保测试质量。然而,现有技术大多依赖于源代码的分析,使得闭源 SDK 库的 fuzz driver 自动化生成成为一个悬而未决的问题。闭源 SDK 库的 fuzz driver 生成面临两大挑战:
(1)闭源 SDK 库仅有有限的信息可被提取;
(2)API函数之间语义关系复杂,但仍需要保证其正确性。
为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了 APICRAFT,一种自动化 fuzz driver 生成技术。APICRAFT 的核心策略是 collect-combine。首先,APICRAFT 利用程序的静态和动态信息来解析出 API 函数的控制和数据依赖关系。然后,APICRAFT 使用多目标遗传算法组合来对收集到的依赖项进行变异进化来构建高质量的 fuzz driver。我们将 APICRAFT 实现为 fuzz driver自动化生成框架,并使用来自 macOS SDK 的五个攻击面对其进行评估。在评估中,APICRAFT 生成的 fuzz driver 表现出比手动编写的更出色的代码覆盖率,平均提高了 64%。我们进一步使用 APICRAFT 生成的 fuzz driver 进行了长期的 fuzzing。经过大约 8 个月的 fuzzing过程,我们迄今为止在 macOS SDK 中发现了 142 个漏洞和 54 个分配的 CVE,这些漏洞会影响流行的 Apple 产品,例如 Safari、Messages、Preview 等。
嘉宾简介:
林以(@xwlin_roy),蚂蚁安全光年实验室安全研究员,他的研究领域包括虚拟化安全、macOS&Windows系统安全,程序分析以及 fuzzing。他曾在学术界以及工业界顶级安全会议上发表论文与演讲,包括 CCS,Usenix Security以及 BlackHat Asia。他获得过来自 Apple、Qemu、Microsoft以及 Oracle等厂商的致谢。
曲和,蚂蚁安全对抗技术部负责人,从 0 组建光年实验室,主要经验在漏洞挖掘、移动安全等上。
吕涛 中国科学院信息工程研究所研究生

演讲主题:RTFM! Automatic Assumption Discovery and Verification Derivation from Library Document for API Misuse Detection
内容摘要:
在当前的软件开发过程中,开发者通常会使用软件库所提供的API以提高开发效率。开发者在调用API时,需要遵守软件库文档中所规定的约束(我们称之为“调用假设”)。违背API的调用假设被称之为API误用,其会造成严重的软件安全问题,例如释放后使用,空指针解引用以及权限认证错误等。
本项工作主要研究如何更加高效地检测API误用。考虑到自然语言处理技术的快速发展以及其在各个领域产生的显著效果,我们基于该技术,提出了一套系统性的方法来自动化地提取调用假设并将其转化为验证代码,以发现与调用假设相违背的应用程序代码(即API误用)。
本文实现了上述方法的原型Advance,并且在5个常用软件库以及39个软件集合上测试了其有效性。最终Advance发现了193个API误用。
嘉宾简介:
吕涛,中国科学院信息工程研究所研究生。研究方向为漏洞检测,包括模糊测试以及智能化漏洞发现技术研究。研究成果发表于CCS以及USENIX Security等信息安全会议。
王力 蚂蚁金服隐私计算高级算法专家

演讲主题:高性能隐私保护机器学习算法
内容摘要:
演讲主要介绍隐私保护机器学习的相关背景与难点,最近几年,在多方安全计算和同态加密方向的演讲逐渐增多,但是,由于密态计算的复杂度高,通信量大,导致在实际应用中性能难以符合要求,本次演讲讲介绍如何结合机器学习和多方安全计算的计算特性,提升隐私保护机器学习的安全性和计算性能,在保证算法实用性的情况下,做到可证安全。
嘉宾简介:
王力 蚂蚁金服隐私计算高级算法专家,2010年加入阿里云从事搜索算法研究工作;2016年加入蚂蚁金服,从事隐私保护机器学习技术的研究与应用工作,带领团队,在多方安全计算、可信执行环境、同态加密等领域进行深入的研究探索,创建了工业级可用的、适配不同场景的多项隐私保护机器学习方案,并在实际业务场景中取得成功。
乐泰 国防科技大学计算机学院博士研究生

演讲主题:EcoFuzz: Adaptive Energy-Saving Greybox Fuzzing as a Variant of the Adversarial Multi-Armed Bandit
内容摘要:
Fuzzing作为一种高效的漏洞挖掘技术,受到了很多研究人员的关注,特别是近些年兴起的以AFL为代表的Coverage-based Greybox Fuzzing技术。然而,AFL在测试时会分配过多的能量(即种子变异产生的测试用例的数量)给执行高频路径的低质量种子,从而浪费了大量的计算资源。此外,当前研究领域对Coverage-based Greybox Fuzzing技术的调度算法方面的研究还不够深入。
针对于这些问题,本文提出了一种基于Adversarial Multi-Armed Bandit的变异式模型来对Coverage-based Greybox Fuzzing中的调度过程进行建模。
我们首先定义了获胜概率这一概念,它表示对某一种子变异产生执行新代码路径的测试用例的概率。通过获胜概率,我们指出了当前AFL调度算法中的一些问题与挑战。基于此,我们定义了种子集合的三种状态,并开发了自适应的能量调度算法以及基于概率的种子搜索策略。我们在AFL基础上实现了一款自适应能量节约型Greybox Fuzzer——EcoFuzz。我们将EcoFuzz与其他10个工具在 14 个真实程序和 LAVA-M 上进行了对比测试。实验结果表明,相较于AFL,EcoFuzz能够在减少32%测试用例生成数量的情况下,达到214%的路径覆盖率。此外,EcoFuzz还发现了GNU Binutils和其他软件中的12个漏洞。我们还扩展了EcoFuzz来测试一些物联网设备,并在SNMP组件中发现了一个新漏洞。
嘉宾简介:乐泰,国防科技大学计算机学院博士研究生。主要研究方向为模糊测试技术。
陈凯翔,清华大学网络空间研究院博士生

演讲主题:自动化绕过虚函数保护
内容摘要:
虚函数调用是C++用于实现面向对象多态特性的语法基础,在各类大型项目被广泛使用。攻击者可以利用虚函数调用结合漏洞实现控制流劫持,为此,研究者们曾提出不同类型、不同粒度的完整性保护方案用于限制虚函数的间接跳转目标。本次报告系统地介绍现有的虚函数保护理论,指出当下的虚函数调用保护存在被绕过的可能性,并分享结合真实程序和漏洞的调研结果。
嘉宾简介:
陈凯翔,清华大学网络空间研究院博士生,清华大学紫荆花队成员。主要研究方向为安全攻防技术。








